wifi4 wifi5 wifi6 wifi7 are generations of Wi-Fi standards, each offering advancements in speed, capacity, and efficiency to meet evolving connectivity needs. Here’s a detailed explanation of each:
1. Wi-Fi 4 (802.11n)
- Introduced: 2009
- Frequency Bands: 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz
- Maximum Speed: Up to 600 Mbps (with multiple antennas, MIMO).
- Key Features:
- Introduced MIMO (Multiple Input, Multiple Output) technology for better data throughput.
- Operates on both 2.4 GHz (longer range) and 5 GHz (higher speed, less interference) bands.
- Marked the first step toward faster and more reliable wireless connections.
2. Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac)
- Introduced: 2013
- Frequency Band: 5 GHz only
- Maximum Speed: Up to 3.5 Gbps (with MU-MIMO and wide channel bandwidth).
- Key Features:
- Added MU-MIMO (Multi-User MIMO) for simultaneous connections to multiple devices.
- Increased channel bandwidth (up to 160 MHz) for faster data rates.
- Focused on reducing interference and latency in high-density environments.
3. Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax)
- Introduced: 2019
- Frequency Bands: 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz
- Maximum Speed: Up to 9.6 Gbps (theoretical).
- Key Features:
- OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access): Improves efficiency by dividing channels into sub-channels to serve multiple devices simultaneously.
- Supports TWT (Target Wake Time): Reduces power consumption for IoT devices by scheduling data transmissions.
- Enhanced performance in crowded environments like stadiums or apartments with dense networks.
- Improved throughput and latency compared to Wi-Fi 5.
4. Wi-Fi 7 (802.11be)
- Expected Introduction: 2024 (adoption starting earlier).
- Frequency Bands: 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz (optional).
- Maximum Speed: Up to 46 Gbps (theoretical).
- Key Features:
- 320 MHz Channel Width: Doubles the bandwidth compared to Wi-Fi 6, enabling faster speeds.
- 16×16 MU-MIMO: Increased simultaneous data streams for better performance in high-density environments.
- Multi-Link Operation (MLO): Allows devices to use multiple frequency bands simultaneously, reducing latency and increasing reliability.
- Low Latency: Targeted for real-time applications like AR/VR, cloud gaming, and 8K/16K video streaming.
- Backward compatible with previous Wi-Fi generations.
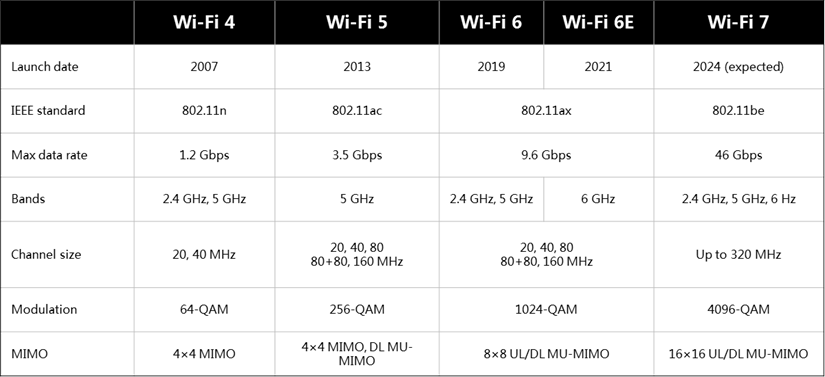
wifi4 wifi5 wifi6 wifi7 Comparison Table
| Feature | Wi-Fi 4 (802.11n) | Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac) | Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) | Wi-Fi 7 (802.11be) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year Introduced | 2009 | 2013 | 2019 | ~2024 |
| Frequency Bands | 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz | 5 GHz | 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz | 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, 6 GHz |
| Max Speed | Up to 600 Mbps | Up to 3.5 Gbps | Up to 9.6 Gbps | Up to 46 Gbps |
| Channel Width | Up to 40 MHz | Up to 160 MHz | Up to 160 MHz | Up to 320 MHz |
| MU-MIMO Support | No | Yes (downlink) | Yes (uplink/downlink) | Yes (uplink/downlink) |
| OFDMA Support | No | No | Yes | Yes |
| Target Wake Time | No | No | Yes | Yes |
| Multi-Link Operation (MLO) | No | No | No | Yes |
| Use Cases | Basic internet | Video streaming, gaming | High-density environments, IoT | AR/VR, 8K/16K video, cloud gaming |
Key Differences
- Speed: Each generation offers higher theoretical speeds, with Wi-Fi 7 providing up to 46 Gbps.
- Efficiency: Technologies like MU-MIMO and OFDMA improve efficiency, especially in multi-device environments.
- Frequency Bands: Wi-Fi 6 and 7 expand to the 6 GHz band for additional spectrum and reduced congestion.
- Latency: Wi-Fi 7 significantly reduces latency, making it suitable for real-time applications.
Summary
- Wi-Fi 4 and Wi-Fi 5 laid the foundation for faster wireless connectivity, but they struggle in crowded environments.
- Wi-Fi 6 introduced significant improvements in efficiency, speed, and IoT support.
- Wi-Fi 7 represents the next leap, targeting ultra-high-speed, low-latency applications for future technologies like AR/VR, cloud gaming, and ultra-high-definition streaming.



